2 R Mechanics
2.1 Installing R
The home page for R is called the Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN). The website is not pretty (see figure 2.1), but it has quite a bit of information on it. It is not the best place to find help on R, although it is one of the best places to get R-related software, tools, and updates.
knitr::include_graphics('images/CRAN-screenshot.png')
Figure 2.1: The Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN) website
Detailed installation instructions are readily available, but here are abbreviated instructions for convenience.
2.1.1 Windows
NOTE: See Windows installation instructions for more detail. Install R and RStudio as regular users.
To install R, visit the Windows base distribution page. Click on the Download R-3.4.0 for Windows link (or use the latest version available). Click on the installer and make the default selection for each option.
To install RStudio, visit the RStudio download page. Click on the current RStudio release for Windows link. Click on the installer and follow default instructions.
2.1.2 Mac
NOTE: See R for Mac OS X for more detail.
To install R, visit the R for Mac OS X. Click on the the R-3.4.0.pkg link (or use the latest version available). Click on the installer and follow default instructions.
To install RStudio, visit the RStudio download page. Click on the current RStudio release for Windows link. Click on the installer and follow default instructions.
2.1.3 Linux
NOTE: See distribution-specific instructions for additional detail.
On debian-based systems, the easiest way to install R is through a package manager manager, run under an administrator account. On Linux one usually needs to install R packages from source, and R package source often contains C, C++, or Fortran code requiring a compiler and -dev versions of various system libraries. It is therefore convenient to install the -dev version of R.
sudo apt-get install r-base r-base-devWhen installing source packages, it may be necessary to have access to the -dev version of various system libraries. Many of these are installed as dependencies of r-base-dev; other common examples include the xml and curl libraries
sudo apt-get install libxml2-dev
sudo apt-get install libcurl-devNote in particular the use specification of libraries (the lib prefix) and the use of the -dev version.
To install RStudio, visit the RStudio download page. Download the appropriate archive for your OS. On Ubuntu, install the .deb installer with
sudo dpkg -i rstudio-1.0.136-amd64.deb2.2 Starting R
How to start R depends a bit on the operating system (Mac, Windows, Linux) and interface. In this course, we will largely be using an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) called RStudio, but there is nothing to prohibit using R at the command line or in some other interface (and there are a few). A screenshot of the interface is shown in figure 2.2.
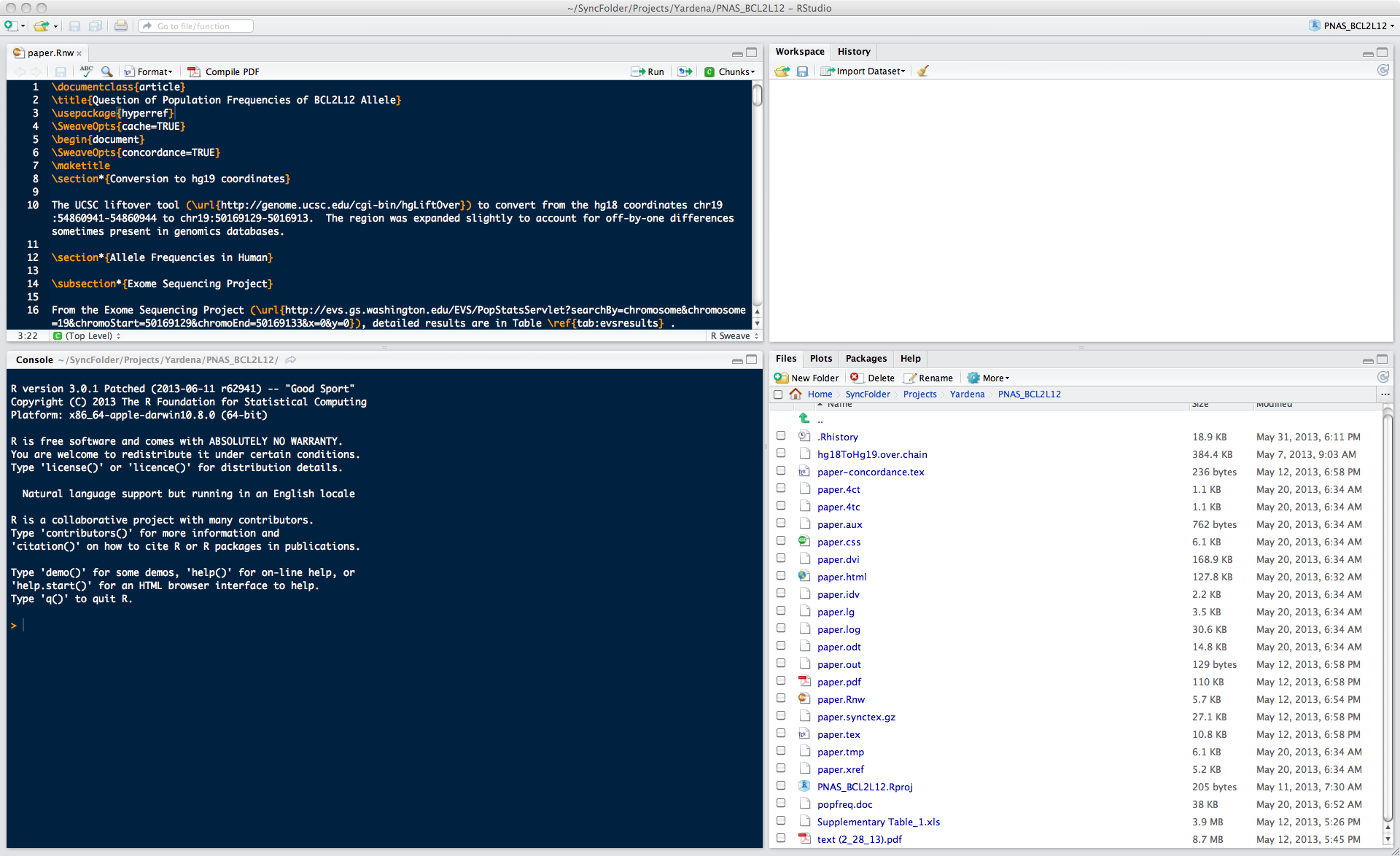
Figure 2.2: The Rstudio interface